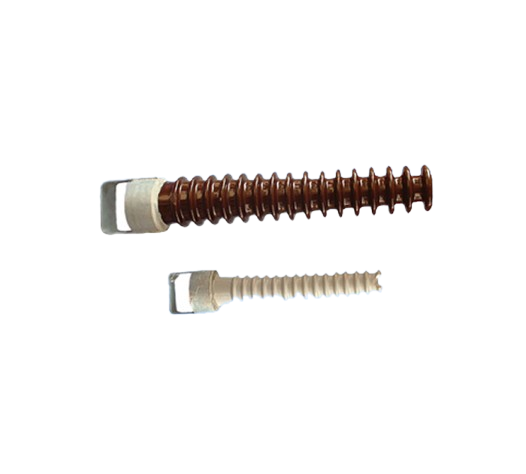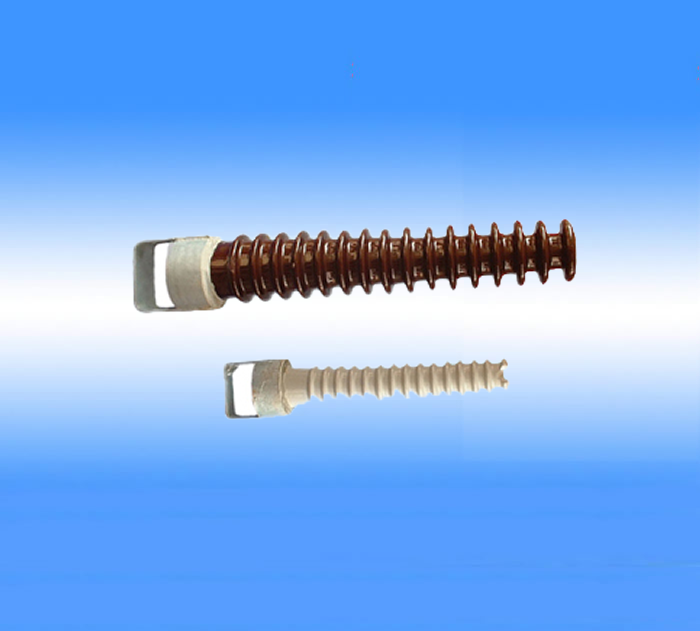
High voltage line porcelain cross-bond insulator manufacturer
Brand: lixiong
- Description
- Installation
1. Overview
It is used for insulation and support wires in high-voltage overhead power lines with nominal voltage of 35kV and below, frequency not exceeding 100Hz, and altitude not exceeding 1000m.
The ambient temperature of the insulator installation site is -40℃~+40℃.
The ambient temperature of the insulator installation site is -40℃~+40℃.
2. Structural characteristics
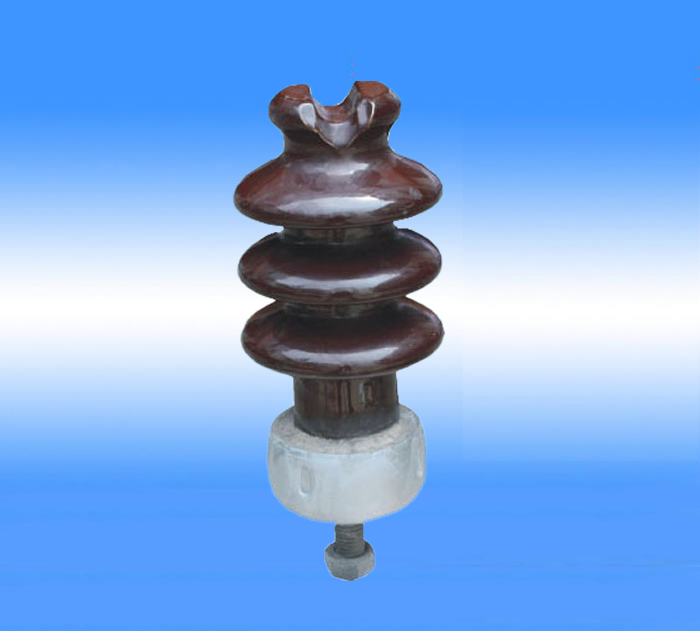
The porcelain cross-bar insulator is a conical or cylindrical porcelain insulator structure that plays the role of both the cross-bar and the insulator. In addition to having the same fixed
wire and the function of insulating the ground as ordinary line insulators, it can also replace iron or wooden cross-bars in whole or in part. This insulator was developed in China to save cross-burden materials (metals, cement
and wood) and adapt to the needs of agricultural power lines construction. It can be installed horizontally or vertically, so it can also reduce the tower height and simplify the tower structure compared to disk insulators or long rod insulators
. Since the first porcelain cross-dan line was put into operation in 1963, this line has developed rapidly over the past few decades.
Currently, 110kV and below lines, especially 6-35kv lines, have been widely promoted and adopted.
There are two types of pure porcelain and glue-mounted ones in the beginning of development.
Pure porcelain structure is a solid porcelain piece with a mounting hole at the root. When used, the installation hole is pressed through the screw and is pressed with a press plate. When pressing, the porcelain piece and the iron piece should be padded with a liner (such as asbestos cloth)
, and the press plate should be pressed with a spring washer. However, this structure has been eliminated due to its low strength and poor operation.
The adhesive-mounted structure is made of solid porcelain and a flange glued with adhesive agent. The flange is equipped with mounting holes for installation through screws.
The porcelain crossbars with medium voltage and above voltage levels are equipped with metal accessories (flanges). In order to buffer the impact force generated when the line is broken, there are also stabilization screw holes on the flange. When the load used exceeds
the strength of , the stabilization screws are cut and the porcelain cross-bar rotates around the installation hole, thereby increasing the slack of the wire, reducing the tension of the wire, and avoiding insulator breakage or rolling rod accidents. The stabilization screws during normal operation
can overcome the wire tension difference on both sides that exist under normal circumstances. There are no stabilizing screws at the pure porcelain root. At this time, the friction force of the installation part overcomes the tension difference between the wires on both sides.
When the wire is broken, it can also rotate around the installation hole. There is also an elastic pad (usually linoleum paper) between the adhesive-mounted structural flange and the end surface of the porcelain piece to reduce thermal stress. Flange is generally made of forged cast
Cast iron, it can also be welded by steel plates, and the surface of the metal accessories is hot-dip galvanized. The glue is prepared from silicate cement and quartz sand no less than 42.5.
There are two types of porcelain cross-bond insulators: horizontal installation and vertical installation. There are two types of wire binding: direct binding and warp clamp fixation. If the insulator is installed horizontally, the wire
is tied to the side groove of the head of the porcelain piece with a thin metal wire, and the insulator can not be made out of the top groove; if the insulator is installed upright, the wire is tied to the top groove of the porcelain piece. Therefore, if
the top-phase porcelain cross-bar insulator is installed upright during operation, the manufacturer will produce a part of the specification with a top groove for this insulator. Another type of fixed wire is that the porcelain head
has a connecting piece to clamp the wire.
my country's porcelain cross-bond insulator is actually a circuit column insulator, a circuit column insulator that can rotate in an accident.
Compared with ordinary line insulators with the electrical and mechanical properties of porcelain cross-burst insulators of the same voltage level, the characteristics are:
(1) The insulation distance and creepage distance of porcelain cross-burst are relatively large, and the 50% full-wave impact flashover voltage and dry and wet industrial strobe flashover voltage are higher;
(2) The porcelain body of porcelain cross-burst is relatively long and the mechanical bending strength is low. After considering the safety and reliability coefficient, the maximum allowable load is generally
smaller than that of ordinary line insulators of the same voltage level, so porcelain cross-burst is not suitable for lines with larger wire cross-sections and distances.
Compared with distribution lines equipped with ordinary insulators, the main advantages of the porcelain cross-bar distribution lines are:
(1) The rotatable structure is adopted. When the line is broken, the unbalanced wire tension will cause the porcelain cross-bar to rotate, thereby effectively alleviating the expansion of line breakage accidents;
(2) The insulation level and lightning resistance of the line are relatively high, and the accident rate is low;
(3) The porcelain body is easily washed by wind and rain, has good self-cleaning properties, and will not break down, and has a small replacement and maintenance amount;
(4) It is easy to construct and install, and when the rod is as high as the wire can be increased to the ground distance of about 0.3 to 2.2m;
(5) Save raw materials such as steel and wood, and can reduce the cost of single-base pole tower by 10% to 50%.
wire and the function of insulating the ground as ordinary line insulators, it can also replace iron or wooden cross-bars in whole or in part. This insulator was developed in China to save cross-burden materials (metals, cement
and wood) and adapt to the needs of agricultural power lines construction. It can be installed horizontally or vertically, so it can also reduce the tower height and simplify the tower structure compared to disk insulators or long rod insulators
. Since the first porcelain cross-dan line was put into operation in 1963, this line has developed rapidly over the past few decades.
Currently, 110kV and below lines, especially 6-35kv lines, have been widely promoted and adopted.
There are two types of pure porcelain and glue-mounted ones in the beginning of development.
Pure porcelain structure is a solid porcelain piece with a mounting hole at the root. When used, the installation hole is pressed through the screw and is pressed with a press plate. When pressing, the porcelain piece and the iron piece should be padded with a liner (such as asbestos cloth)
, and the press plate should be pressed with a spring washer. However, this structure has been eliminated due to its low strength and poor operation.
The adhesive-mounted structure is made of solid porcelain and a flange glued with adhesive agent. The flange is equipped with mounting holes for installation through screws.
The porcelain crossbars with medium voltage and above voltage levels are equipped with metal accessories (flanges). In order to buffer the impact force generated when the line is broken, there are also stabilization screw holes on the flange. When the load used exceeds
the strength of , the stabilization screws are cut and the porcelain cross-bar rotates around the installation hole, thereby increasing the slack of the wire, reducing the tension of the wire, and avoiding insulator breakage or rolling rod accidents. The stabilization screws during normal operation
can overcome the wire tension difference on both sides that exist under normal circumstances. There are no stabilizing screws at the pure porcelain root. At this time, the friction force of the installation part overcomes the tension difference between the wires on both sides.
When the wire is broken, it can also rotate around the installation hole. There is also an elastic pad (usually linoleum paper) between the adhesive-mounted structural flange and the end surface of the porcelain piece to reduce thermal stress. Flange is generally made of forged cast
Cast iron, it can also be welded by steel plates, and the surface of the metal accessories is hot-dip galvanized. The glue is prepared from silicate cement and quartz sand no less than 42.5.
There are two types of porcelain cross-bond insulators: horizontal installation and vertical installation. There are two types of wire binding: direct binding and warp clamp fixation. If the insulator is installed horizontally, the wire
is tied to the side groove of the head of the porcelain piece with a thin metal wire, and the insulator can not be made out of the top groove; if the insulator is installed upright, the wire is tied to the top groove of the porcelain piece. Therefore, if
the top-phase porcelain cross-bar insulator is installed upright during operation, the manufacturer will produce a part of the specification with a top groove for this insulator. Another type of fixed wire is that the porcelain head
has a connecting piece to clamp the wire.
my country's porcelain cross-bond insulator is actually a circuit column insulator, a circuit column insulator that can rotate in an accident.
Compared with ordinary line insulators with the electrical and mechanical properties of porcelain cross-burst insulators of the same voltage level, the characteristics are:
(1) The insulation distance and creepage distance of porcelain cross-burst are relatively large, and the 50% full-wave impact flashover voltage and dry and wet industrial strobe flashover voltage are higher;
(2) The porcelain body of porcelain cross-burst is relatively long and the mechanical bending strength is low. After considering the safety and reliability coefficient, the maximum allowable load is generally
smaller than that of ordinary line insulators of the same voltage level, so porcelain cross-burst is not suitable for lines with larger wire cross-sections and distances.
Compared with distribution lines equipped with ordinary insulators, the main advantages of the porcelain cross-bar distribution lines are:
(1) The rotatable structure is adopted. When the line is broken, the unbalanced wire tension will cause the porcelain cross-bar to rotate, thereby effectively alleviating the expansion of line breakage accidents;
(2) The insulation level and lightning resistance of the line are relatively high, and the accident rate is low;
(3) The porcelain body is easily washed by wind and rain, has good self-cleaning properties, and will not break down, and has a small replacement and maintenance amount;
(4) It is easy to construct and install, and when the rod is as high as the wire can be increased to the ground distance of about 0.3 to 2.2m;
(5) Save raw materials such as steel and wood, and can reduce the cost of single-base pole tower by 10% to 50%.
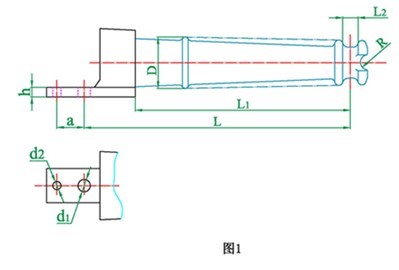
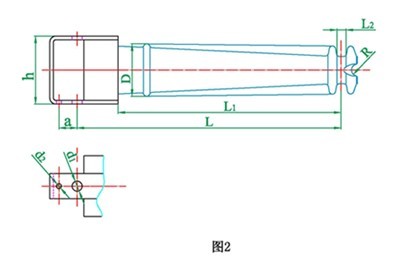
3. Model description
JB/T 8179-1999 standard stipulates (old model):
S—— porcelain cross-bond insulator;
the numbers 1, 2, 3… after S are the design sequence numbers;
the numbers after "-" are the rated voltage value, kV;
the numbers after "/" are the rated bending and failure load value, kN.
GB/T 21206-2007 standard stipulates (new model):
RA - a line column insulator used as a cross-load;
the number after RA represents the bending failure load value, kN;
the letter E or J represents the outer or inner glue assembly of the metal accessories;
the letter T, C, and H respectively represents the top binding type, the top clamp type installed upright or the top clamp type installed horizontally;
the number of the suffix represents the specified lightning impact withstand voltage value, the peak value kV;
the letter N or L of the suffix represents the standard and long creepage distances respectively.
S—— porcelain cross-bond insulator;
the numbers 1, 2, 3… after S are the design sequence numbers;
the numbers after "-" are the rated voltage value, kV;
the numbers after "/" are the rated bending and failure load value, kN.
GB/T 21206-2007 standard stipulates (new model):
RA - a line column insulator used as a cross-load;
the number after RA represents the bending failure load value, kN;
the letter E or J represents the outer or inner glue assembly of the metal accessories;
the letter T, C, and H respectively represents the top binding type, the top clamp type installed upright or the top clamp type installed horizontally;
the number of the suffix represents the specified lightning impact withstand voltage value, the peak value kV;
the letter N or L of the suffix represents the standard and long creepage distances respectively.
4. Technical standards
GB/T 1001.1-2003 "Porcelain or glass insulator components for AC systems with nominal voltage higher than 1000V - Definition, Test Methods and
Determination Criteria"
GB/T 21206-2007 "Properties of Line Column Insulators"
JB/T 9676-1999 "Technical Conditions of High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage" JB/T 8179-1999 "Size and Characteristics of High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross -High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain
Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage
Determination Criteria"
GB/T 21206-2007 "Properties of Line Column Insulators"
JB/T 9676-1999 "Technical Conditions of High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage" JB/T 8179-1999 "Size and Characteristics of High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross -High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain
Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage Porcelain Cross-High Voltage
Request a Quote
We will deliver a solution and quote that best suits your business needs